As a trader or investor, it is important to have a good understanding of market indicators and ratios that can help you make informed investment decisions.
An additional important aspect to consider is the tendency to overlook the correlation between two markets’ trading patterns. Two widely followed and popular ratios are the Gold to Silver Ratio and the Dow to Gold Ratio.
How many OZ Silver for 1 OZ Gold?

View the Gold to Silver Ratio over the last 100 Years hereThe gold to silver ratio is measuring of how many ounces of silver it takes to buy one ounce of gold (XAUUSD). It is showing the relative value of gold compared to silver. A higher ratio is indicating gold is relatively more expensive compared to silver, and the lower ratio is showing the opposite.
This does not mean both metals cannot decrease in value at the same time. If both metals are falling in price, the ratio can also increase if Gold is falling less than silver. By knowing where the ratio is trading is making it easier to see what metal to favour, or (dis)favour both!
Pros:
Historical significance: The Gold to Silver Ratio has a long history of use in the precious metals market and is considered a reliable indicator of market trends.
Diversification: By using the Gold to Silver Ratio, traders and investors can diversify their investment portfolios beyond just one precious metal.
Relative value: The ratio provides a means of determining the relative value of gold and silver and can be used to make informed investment decisions.
Cons:
Limitations: The Gold to Silver Ratio is one of many factors that should be considered when making investment decisions. Other factors such as market conditions, economic indicators, and geopolitical events can impact the price of both metals.
Market volatility: The price of gold and silver can be volatile, and the ratio can change quickly, making it difficult for traders and investors to make timely decisions.
How many OZ Gold for the quote of DJIA?
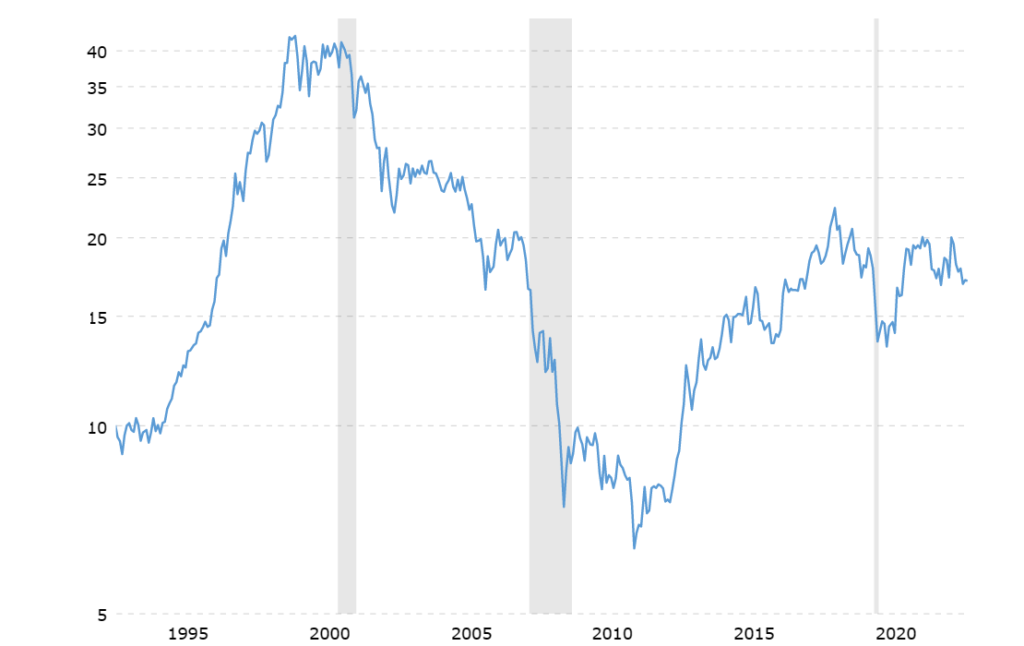
View the Dow to Gold Ratio over the last 100 Years hereThe Dow to Gold ratio is measuring how many ounces of gold it takes to buy the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) index. It is showing the relative value of stocks (represented by the DJIA) compared to gold. A higher ratio is indicating stocks are relatively more expensive compared to gold, and a lower ratio is showing the opposite.
This does not mean both markets cannot decrease at the same time. If both markets are falling, the ratio can also increase if DJIA is falling less than Gold. By knowing where the ratio is trading is making it easier to see what market to favour, or (dis)favour both!
Pros:
Long-term view: The Dow to Gold Ratio provides a long-term view of market trends and can be used by investors to make strategic investment decisions.
Investment diversification: By using the ratio, investors can diversify their investment portfolios beyond just one asset class.
Market sentiment: The ratio can be used as an indicator of broader market sentiment, with a higher ratio potentially signaling a preference for safety and a lower ratio signaling a preference for riskier assets.
Cons:
Limitations: Like the Gold to Silver Ratio, the Dow to Gold Ratio is just one of many factors that should be considered when making investment decisions.
Fluctuations: The ratio can fluctuate widely and can be influenced by a variety of factors, including changes in the price of gold, the stock market, and economic conditions.
Overall
Both the Gold to Silver Ratio and the Dow to Gold Ratio are popular ratios that can be used by traders and investors to make informed investment decisions. The ratios should not be used in isolation. By knowing the relative pricing of two markets, it can be more manageable to make wise trading strategies. Following ratios can be an awakener of when to be active in markets.
More on Gold to Silver
Platinum to Gold Ratio
For cooperatives, ratios and you are welcome to email short @ shortmarkets.com
